Python実践データ分析100本ノック第2章より
目次
商品名の揺れ
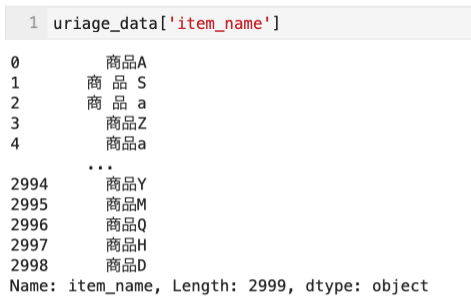
現状のユニークアイテム一覧
pd.unique(uriage_data['item_name'])
# その数
len(pd.unique(uriage_data['item_name']))
# > 99半角全角スペース、大文字小文字の混在を解消する
# データの揺れは「全角半角スペース」と「大文字小文字」の混在が原因、これを解消する
uriage_data['item_name'] = uriage_data['item_name']\
.str.upper()\
.str.replace(" ", "")\
.str.replace(" ", "")print(pd.unique(uriage_data['item_name']))
print(len(pd.unique(uriage_data['item_name'])))
# uriage_data.sort_values(by=['item_name'], ascending=True)でソートしてもよい
金額欠損値の補完
今回の流れ
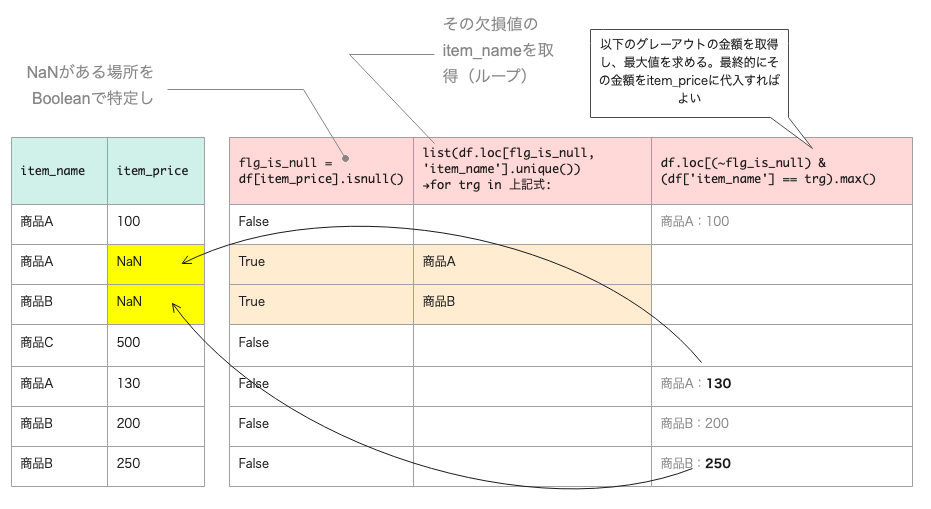
- 欠損値の場所を特定
- その商品名を取得(ユニークで)
- 逆に欠損値でない場所の、その商品名を使えば、金額(price)がわかる
(ここでは時期のより金額が変わるが最大値を採用している) - そのpriceを欠損値の場所に代入する
- 最後、nullがないか検証する
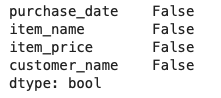
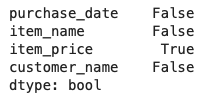
# データ全体に欠損値が含まれているか確認(列に1つでも欠損値を含むか)
uriage_data.isnull().any(axis=0)
# 列「item_price」の欠損値の場所
flg_is_null = uriage_data['item_price'].isnull()
flg_is_null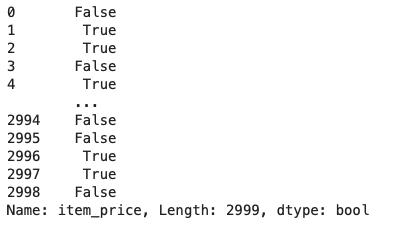
# 欠損値のある行の列「item_name」を取得し、そのユニーク「item_name」を取得
list_item_name_contain_null = list(uriage_data.loc[flg_is_null, 'item_name'].unique())
print(list_item_name_contain_null)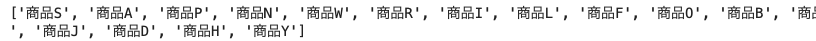
# 最初の図を参照
for trg in list_item_name_contain_null:
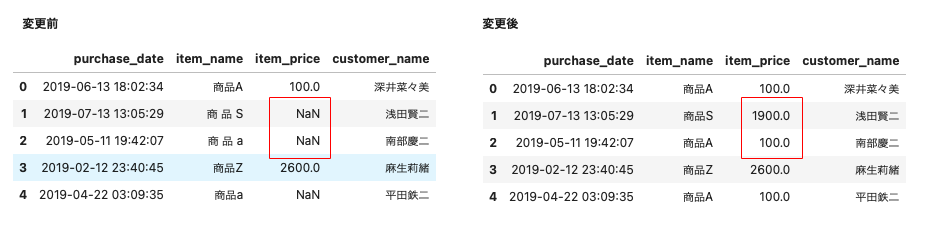
price = uriage_data.loc[(~flg_is_null) & (uriage_data['item_name'] == trg), 'item_price'].max()
uriage_data['item_price'].loc[(flg_is_null) & (uriage_data['item_name'] == trg)] = price
uriage_data.head()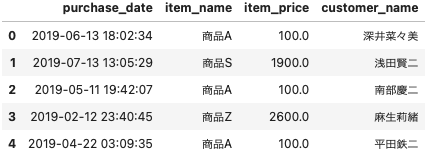
# 最後に検証
uriage_data.isnull().any(axis=0)